The World Health Organization (WHO) opens this space with a real slam dunk: cancer is the second leading cause of death worldwide. Nearly 9 million people died from this group of diseases in 2015. On the other side of the coin, up to 90 % of patients diagnosed quickly with some types of cancer survive without major problems.
Cancer is not just a number, a statistic or a graph. Each of those 8.8 million people who ended up dying (and those who are alive today) have faced a veritable titan of fear, pain and worry: a tumor is not the end of the road, but it does take infinite courage to fight it. Unfortunately, cancer is undoubtedly the defining pathology of the 21st century.
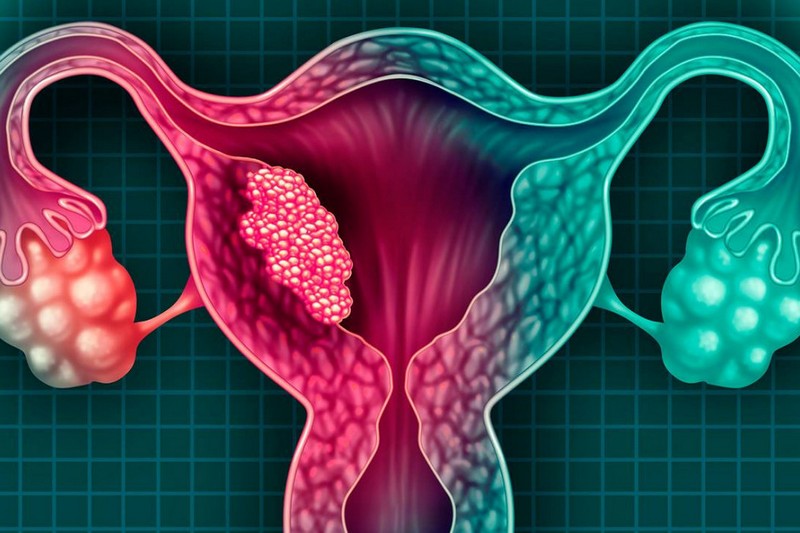
The key to successful treatment of a malignant tumor is rapid detection, and this is where the media come into play. It is our duty to inform the general public about the symptoms, prevalence and treatments available for any type of cancerous process, as no pain or discomfort over a long period of time should be taken lightly. In this space we tell you everything you should know about cervical cancer (CCU).
What is cervical cancer?
According to the National Cancer Institute (NIH), cancers are defined as diseases in which abnormal cells multiply uncontrollably and invade nearby tissues. In the worst cases, these cells can enter the bloodstream or lymphatic system and move to other organs, an event known as metastasis.
On the other hand, cervical cancer is different from malignant neoplasms originating in other parts of the uterus and, therefore, has a different treatment. and, therefore, has a different treatment and prognosis. These malignant tumors (like the rest) are caused by mutations in the DNA of the cells which, instead of dividing and dying naturally, grow uncontrollably causing the mass of tissue.
It should be noted that, before the appearance of the cancer itself, a series of pre-malignant changes in the cells manifest themselves in the patient. We can distinguish 3 different phases:
- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN1).affects less than 1⁄3 of the epithelial tissue. Approximately 70% of these lesions disappear, while about 6% may eventually become more severe. They do not usually require treatment.
- Mid-grade intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN2).The epithelium is thickened. Most patients who present require treatment.
- Carcinoma in situ (CIN3)The entire epithelium is affected. Approximately 20% of women with CIN3 eventually develop invasive cancer within 10-15 years.
The incidence rate of this disease has increased by 50% between 1975 and 2015. As alarming as this may sound, this is good news: the means of detection are much more sophisticated and, in many cases, a solution can be put in place for precancerous lesions before they become complicated.
What are their causes?
The triggers for cervical cancer are not entirely clear, but you may be surprised to learn that human papillomavirus (HPV) is directly linked to 70% of cervical cancer cases.. It is estimated that there are more than 100 strains of HPV, of which at least 14 are oncogenic (have cancer-causing potential).
The subtypes of most concern are HPV 16 and HPV 18, which have been linked on multiple occasions to cervical cancer. 70% of women infected with this virus are cured within 1 year without any necessary treatment, while 90% of patients are rid of the infection in less than 2 years. Unfortunately, 5-10% of infected women have recurrent infectious episodes, which promotes the appearance of precancerous lesions. Fortunately, these lesions take 10-15 years to develop into cancer (if they do), which is why there is plenty of room for action.
Beyond HPV, cervical cancer has also been linked to factors such as smoking, cancer of the cervix has also been linked to factors such as smoking, having Sexually Transmitted InfectionsHaving recurrent Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs), a weakened immune system, and the use of certain now-banned drugs. In general, the best thing to do to avoid this type of cancer is to practice safe sex and have regular gynecological checkups.
Symptoms of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer in its early stages does not produce any symptoms, like the vast majority of neoplastic tumors. When it is found in more advanced stages, the most common clinical signs are as follows:
- Vaginal bleeding during intercourse, between periods or after menopause, i.e., times when bleeding should not occur.
- Bloody, watery vaginal discharge that may have a foul odor.
- Pelvic pain or pain during intercourse.
- Persistent back pain with no apparent cause.
It should be noted that, in most cases, if you have any of these symptoms, it is possible that you are dealing with a pathology other than cancer. Various etiological agents famous in the world of STIs (trichomoniasis, candidiasis and vaginosis, among others) can show themselves with foul-smelling purulent secretions, which is why you should not be overly alarmed if you have recognized yourself in any of these points. Even so, it goes without saying that in the event of any of these events, a visit to the gynecologist is a must.
Treatment
There are different types of treatment for cervical cancer and its application depends entirely on the state of the tumor and the patient himself.. Five types of standard procedures are used: radiotherapy, immunotherapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy and surgery.
In the initial stage of treatment, surgery is usually the way to go. During this, removal of the tumor alone, the entire cervix or the cervix and uterus is considered. The choice will depend on the size of the tumor and its extent. In locally advanced cancers, radiotherapy and chemotherapy techniques are usually used at the same time to kill the tumor cells.
You are not alone
We know that cancer is a socially forbidden term and that, in many cases, for fear of receiving bad news, it is much easier to go on with life as if nothing were wrong. We cannot overemphasize that uterine cancer can be detected long before it appears and that, without a doubt, the best treatment is based on prompt diagnosis and action.
When detected at an early stage the survival rate for women with uterine cancer is very high, at 92%.. The mortality rate between 1975 and today has been reduced by 50%, solely due to early detection methods and preventive treatment. In these cases, it is no good turning a deaf ear to reality: it is estimated that this type of neoplasm is the fourth most common cancer in women worldwide, with some 570,000 new cases per year (6.6% of all female cancers).
With these data we do not intend to scare any reader, but it is important to point out that proper monitoring, regular visits to the gynecologist and absolute transparency on your part when going to the doctor can literally save your life. Having cancer is a race against the clock, and if you are caught early, victory is almost assured.
Summary
As you may have read in these lines, cervical cancer is one of the most common malignant neoplasms in women, especially if we take into account that other types of cancer higher up the list are caused by exogenous factors (such as smoking or obesity, for example). Fortunately, precancerous lesions are detectable up to 10-15 years before the appearance of the malignant tumor and can therefore be treated with great efficacy..
Although the causes of cervical cancer are not yet fully understood, it is clear that the human papillomavirus and recurrent STIs play an essential role in its occurrence. Therefore, the best prevention we can offer you is to practice safe sex at all times of your life. Against cancer, all prevention is not enough.